
Managerial accountants use information relating to the cost and sales revenue of goods and services generated by the company. Cost accounting is a large subset of managerial accounting that specifically focuses on capturing a company’s total costs of production by assessing the variable costs of each step of production, as well as fixed costs. It allows businesses to identify and reduce unnecessary spending and maximize profits. Featuring versatile curricula that integrate business acumen with quantitative and communication skills, managerial accounting concentrations train students to use financial data to inform organizational decision-making. With professional certifications and experience, this concentration can support students pursuing high-paying financial manager jobs, which boast a median annual salary of $129,890, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
Product costing and valuation
Throughout my career, I’ve worked with many professionals in managerial accounting — from cost accountants to CFOs. The primary focus of managerial accounting is ensuring that a company has all the information required to make sound decisions that limit risk and maximize profits. Using this information, accounting professionals create budgets, policies, strategies, plans, and recommendations that they then present to the executive leadership teams at their organizations. The ultimate goal of managerial accounting is to support intelligent decision-making.
Gain professional experience.
Advisory accounting also supports risk management through scenario planning and financial modeling. Accountants help businesses simulate various risk scenarios, such as economic downturns or market shifts, and assess their financial impacts. This approach allows leaders to evaluate potential outcomes of different strategies and make informed decisions about managing risks while pursuing growth. The controls that were put into place to coordinate the implementation of a particular company plan must be evaluated so that success can be measured, or corrective action can be taken. Consider Daryn’s Dairy’s one-year plan to increase market share by selling products in \(10\) percent more stores in the states in which the company currently operates.
Seamless, Local-Desktop-Like Experience
Managerial accounting is the process of analyzing, interpreting, and measuring an organization’s financial processes. This type of accounting uses data to help provide leaders with insight for strategic financial planning that aligns with that organization’s goals and business objectives. In managerial accounting, the main focus will be on financial decisions that affect the internal workings of a company. For example, managerial accountants may help leaders decide whether or not to raise the cost of goods and services. The field of management accounting employs financial information and skills to guide internal management and planning.
Costs must be determined and recorded accurately, systematically, and on a timely basis. Activity-based costing is a system that is combined with the other two methods to identify and measure costs more specifically. Since human, financial, and time resources are limited, managers must select from among many alternatives, foregoing other options.
How to get a job in managerial accounting
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) in accounting are detailed, written instructions that outline the steps required to complete specific tasks or processes within the accounting department.
- Allowing them to contribute ideas and shape the firm fosters a sense of belonging.
- In this article, learn about managerial accounting, the different types, the education requirements, and how to enter this career field.
- Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.
- Management may want to consider abandoning the pontoon line and using that additional capacity to produce one of the other more profitable lines.
Both the controller and the treasurer report directly to the company’s head of finance. While the controller’s functions involve internal finance and accounting, the treasurer’s responsibilities involve external finance and cash functions. Managerial accounting, or management accounting, is the branch of accounting that focuses on providing information for internal parties – i.e. the company’s management, to aid in decision-making. The most significant recent direction in managerial accounting is throughput accounting; which recognizes the interdependencies of modern production processes.
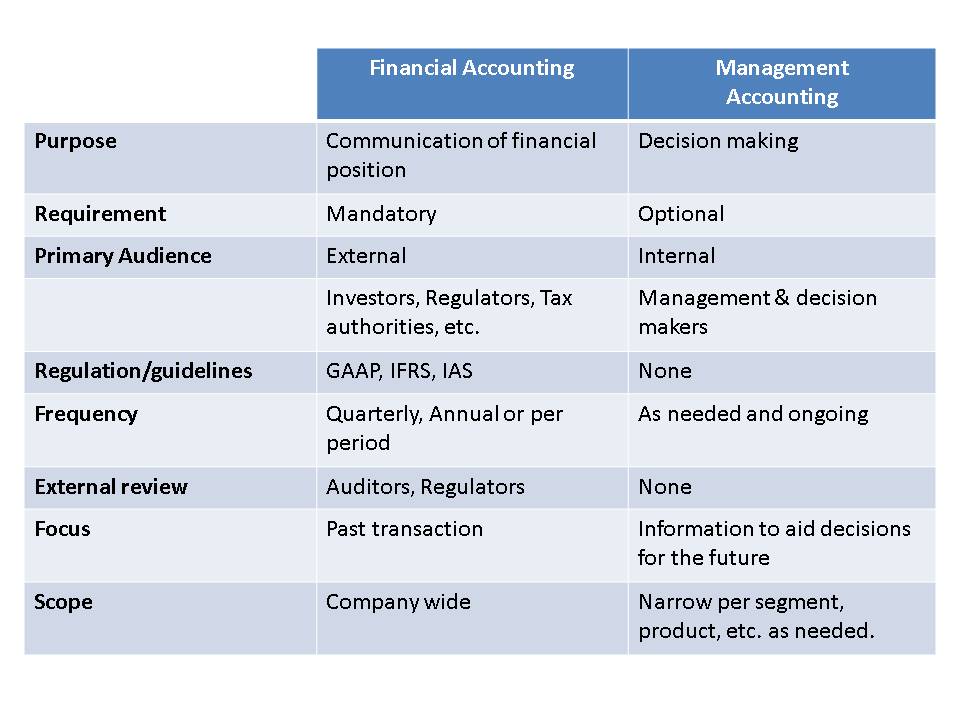
The three main types of accounting for businesses are tax accounting, financial accounting and management accounting. Many new businesses perform only tax accounting so they can file their tax returns. As the company grows, however, financial and management accounting become increasingly important. In business, financial accounting refers to the act of recording a company’s financial transactions, which are typically examined by investment banking analysts and shareholders of public corporations. A separate practice known as managerial accounting refers to the discipline of record-keeping with an eye towards budgeting and performance measurement, typically conducted by managers.
A financial analyst’s main duty is to examine data to determine outcomes and opportunities for business investments and decisions. Financial analysts will track and analyze financial processes for companies, support other departments, and use financial data to create how to create an invoice in quickbooks budgets and forecasts. With cloud accounting, businesses can manage accounts, track expenses, generate invoices, and access real-time financial data with ease. This approach saves time and money, reduces errors, and makes financial management far more flexible.





