Collectibles gain or loss with respect to a pass-through interest that is treated as capital interest gain or loss must also be included in the 28% Rate Gain Worksheet. To determine the amount of gain or loss described in section 864(c)(8), generally, a foreign transferor must first determine its outside gain or loss on the transfer of a partnership interest. For this purpose, outside gain or loss is determined under all relevant provisions of the Code and regulations thereunder. These rights must have arisen under a contract or agreement that existed at the time of sale or distribution, even though the partnership may not be able to enforce payment until a later date. For example, unrealized receivables include accounts receivable of a cash method partnership and rights to payment for work or goods begun but incomplete at the time of the sale or distribution of the partner’s share. A partnership liability is a nonrecourse liability if no partner or related person has an economic risk of loss for that liability.
1 Calculation of Interest on Drawings
When working on your own, you have to choose where to place your time and energy. This means that you might not be able to pursue all the business opportunities that arise. But when duties are shared among partners, there is a better ability to increase productivity and pursue new opportunities.

What is a partnership agreement?
As the amount is guaranteed, it must be dealt with through a credit entry in the partner’s account (usually the current account) before the residual profit is shared. This information will be provided to the notifying transferor on or before the due date (with extensions) for issuing Schedule K-1 (Form 1065), Partner’s Share of Income, Deductions, Credits, etc. The foreign transferor only includes in income the lower of the outside amount and the deemed sale effectively connected amount. This determination is made separately with respect to capital gain or loss and ordinary gain or loss. For example, a foreign transferor would compare its outside ordinary gain to its aggregate deemed sale effectively connected ordinary gain, treating the former as effectively connected gain only to the extent it does not exceed the latter.
What Types of Businesses Are Best-Suited for Partnerships?
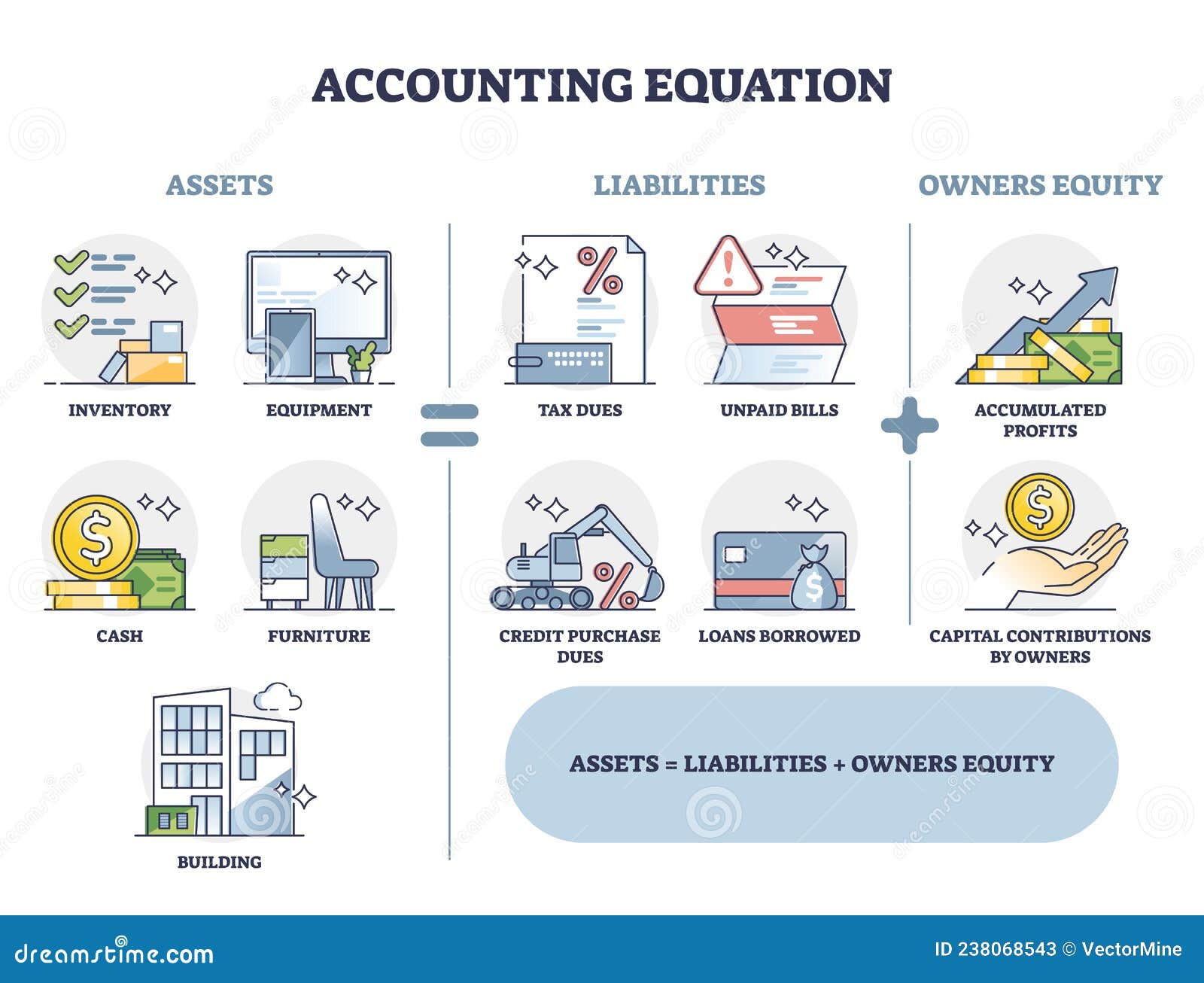
Interest on capital is a loss or expense to the firm and thus debited to Interest on capital account and finally transferred to Profit and Loss Appropriation Account. And it is an income or gain to the partners and their Capital Account or Current Account is credited with the amount of interest. The partnership deed usually mentions the method of maintaining capital accounts of partners. There are two methods by which capital accounts are maintained i.e., Fixed Capital and Fluctuating Capital. A partnership organisation maintains accounts of its transactions in the same manner as a Sole Trader ship.

Selecting a ratio based on capital balances may be the mostlogical basis when the capital investment is the most importantfactor to a partnership. These types of ratios are also appropriatewhen the partners hire managers to run the partnership in theirplace and do not take an active role in daily operations. The lastthree approaches on the list recognize differences among partnersbased upon factors such as time spent on the business or fundsinvested in it. Dissolving a partnership is a significant event that requires meticulous planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition. The dissolution process typically begins with a formal decision by the partners, often guided by the terms outlined in the partnership agreement. This decision can be triggered by various factors, such as the expiration of the partnership term, mutual agreement, or specific events like the death or bankruptcy of a partner.
Tax information for partnerships
A partnership agreement outlines how the business will operate and who will be responsible for what roles. Learn how this legal document will set your business up for success. The fastest way to receive a tax refund is to file electronically and choose direct deposit, which securely and electronically transfers your refund directly into your financial account.
- The specifics of profit sharing should be laid out in writing in a partnership agreement.
- In the absence of any agreement between partners, profits and losses must be shared equally regardless of the ratio of the partners’ investments.
- Beginning in tax year 2020, the IRS required partnerships to report their capital accounts on Schedule K-1, Item L, partners’ capital account analysis using the tax basis.
- Adjustments are made for guaranteed payments, as well as for depreciation and other expenses.
- She receives a distribution of $8,000 cash and land that has an adjusted basis of $2,000 and an FMV of $3,000.

If drawings are made at the end of each month, the period is 5 1/2 months for the total amount. Find out the number of months from the date of drawings to the date of closing of the financial year, of each drawing, multiply the amount of drawings with these respective partnership account months, and then find total of the products. If interest on Drawings is to be charged then it is always with reference to time. As said earlier, it is essential to know the amount of drawings, the period and the rate of interest for the calculation of interest.

Compensation for services and capital
Thus, a percentage of profit is paid to a partner for the special work or service done. This commission may be payable before charging such commission or after charging such commission. To the firm it is an income and therefore the Capital or Current Accounts of the partners are debited and Interest on Drawing Account is credited. To make calculation of the interest on Drawings, three things must be present – the interest rates the amount and the period. The current account may show credit and debit balance at the end of the year. If they show Credit balances, they appear on the liability side of the Balance Sheet of the firm along with Fixed Capitals.
Forms & Instructions
If contributed property is subject to depreciation or other cost recovery, the allocation of deductions for these items takes into account built-in gain or loss on the property. However, the total depreciation, depletion, gain, or loss allocated to partners cannot be more than the depreciation or depletion allowable to the partnership or the gain or loss realized by the partnership. A partnership that uses an accrual method of accounting cannot deduct any business expense owed to a cash basis partner until the amount is paid. However, this rule doesn’t apply to guaranteed payments made to a partner, which are generally deductible when accrued. A partner who acquired any part of their partnership interest in a sale or exchange or upon the death of another partner may be able to choose a special basis adjustment for property distributed by the partnership. To choose the special adjustment, the partner must have received the distribution within 2 years after acquiring the partnership interest.
- The amount of the bonus paid by the partnership is distributed among the partners according to the partnership agreement.
- (iv) Transfer 10% of the distributable profit, before distribution, to the Reserve Fund of the firm.
- The interest on capitals comes to Rs. 1,080 (A-Rs.l80, B-Rs.270; C-Rs.360; D-Rs.270) which is distributed to the partners in the profit sharing ratio, which should have been in the capital ratio that is interest on capital.
- The Final Profit then is transferred to Capital Account, m case of Fluctuating Capital System or to Current Account, in case of Fixed Capital System.
- Instead, taxes are passed through to the individual partners to file on their own tax returns, often via a Schedule K.
- Partnerships are often best for a group of professionals in the same line of work where each partner has an active role in running the business.