
On the other hand, the sum of years’ digits can be determined by totaling the digits in every year of the fixed asset’s useful life. For example, if the fixed asset has 5 years of useful life, the sum of years’ digits can be determined to be 15 (5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1). To use the sum of years, a calculation needs to be performed to determine the sum of years depreciation rate using the remaining life expectancy as the numerator and the sum of the digit number of years as the denominator.
Ask Any Financial Question
Where other methods use concepts like standard depreciation rate or using years of useful life, sum of years isn’t as straightforward. To illustrate SYD depreciation, assume that a service business purchases equipment at a cost of $160,000. This asset is expected to have a useful life of 5 years at which time it will be sold for $10,000. This means that the total amount of depreciation will be $150,000 spread over the equipment’s useful life of 5 years. Mega Coffee believes that at the end of the computers’ 5-year useful life, they will be worth $200,000.
Step 2: Numerator
Therefore, the company deducts its balance from the balance of the equipment account in the balance sheet. In simple terms, the company reports the net asset value in the balance sheet. As a small business owner, you are well acquainted with the tax deduction for depreciation. In addition to the tax benefit depreciation provides, it also allows you to track and decrease the value of your assets over their useful life.
What is my company’s balance sheet doing?
To demonstrate how this fraction is worked out, suppose that an asset has a 5-year life. In the first year, the rate is a fraction that has a numerator of 5, the number of years remaining at the beginning of the year. An asset is purchased on 1 July 2020 and has an estimated useful life of 6 years.
- The company decides to depreciate the assets using the SYD method as it faces a fairly harsh tax environment.
- ‘Inc.’ in a company name means the business is incorporated, but what does that entail, exactly?
- For example, on January 1, the company ABC buys a machine that cost $52,000 in order to use for the day-to-day operation.
- To use the sum of years, a calculation needs to be performed to determine the sum of years depreciation rate using the remaining life expectancy as the numerator and the sum of the digit number of years as the denominator.
- The remaining useful life of the fixed asset is determined separately in each year of depreciation in the sum of years’ digits depreciation methods.
Therefore, charging higher depreciation costs early on and decreasing depreciation charges in later years reflects the reality of an asset’s changing economic usefulness over time. The sum of years depreciation method works by depreciating the asset’s depreciable amount by a depreciation factor unique to each year. The depreciable amount is equal to the asset’s total acquisition cost less the asset’s salvage value.
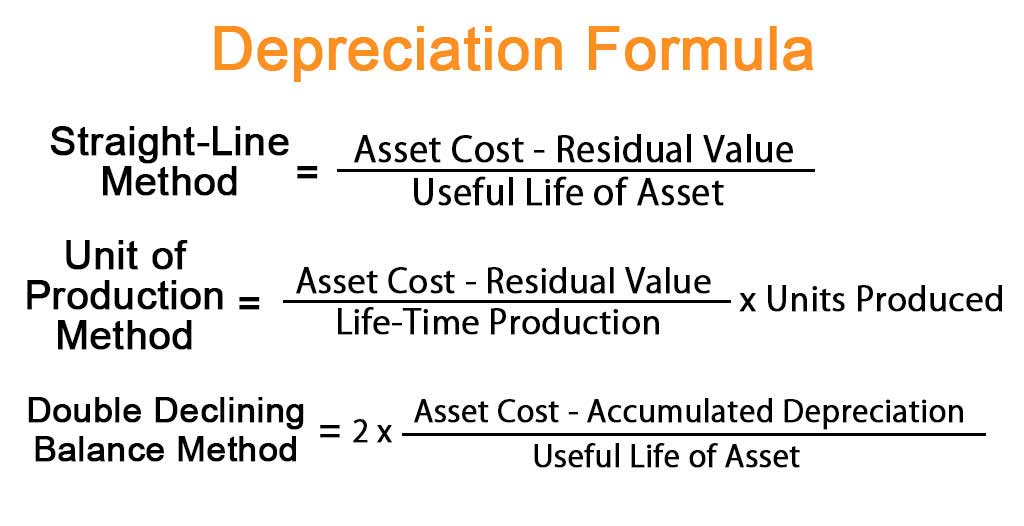
Sum of the years’ digits depreciation method involves calculating depreciation based on the sum of the number of years in an asset’s useful life. The Sum-of-the-Years’ Digits method is a valuable tool for businesses seeking to align depreciation expenses with the actual economic benefits derived from an asset. By front-loading depreciation, the SYD method provides a realistic reflection of an asset’s declining value and utility over time.
It also allows you to take a larger depreciation deduction faster than using straight-line depreciation. What are the pros and cons of sum of the years’ digits versus straight line depreciation. To conclude the Excel sum of years depreciation calculator, available for download below, will calculate the depreciation expense for any asset with a maximum useful life of up to 600 periods. This sum of years depreciation calculator can be used to provide the sum of the years digits depreciation expense for any period in the useful life of an asset up to a maximum of 600 periods.
The same asset, using straight-line depreciation and zero salvage value, would be depreciated at $5,000 per year for five years ($25,000 ÷ 5) until the asset depreciates to zero value. The same company, with the exact same assets, would appear to be earning different amounts of profit and have assets carried at different values on the balance sheet, depending upon which depreciation method was utilized. For example is an asset has a 4 year life and you enter the useful life as 4, then the depreciation will be for each year. In contrast if you enter the useful life as 48 months, then the calculation of the depreciation expense is for each month. The template uses the sum of years digits depreciation formula to calculate the depreciation for each period.
To calculate depreciation charges using the sum of the years’ digits method, you’ll need to first get the depreciable base, which is the cost of the asset. Second, you’ll calculate the salvage value of the asset, which works the same for both the SYD and straight-line depreciation methods. For example, if you buy an asset for $100,000 and it can be sold for an estimated $10,000 at the end of its useful life, the balance subject to depreciation is $90,000, and the salvage value is $10,000. Next, calculate the applicable percentage of depreciation for each year of the asset’s life. Sum of the years’ digits depreciation is the type of depreciation method that allocates the higher cost of the fixed assets in the early year and reduces the depreciation expense in later years as time passes.
For example, on January 1, the company ABC buys a machine that cost $52,000 in order to use for the day-to-day operation. The machine is expected to have 8 years of useful life with a salvage value of $2,000. Due to the nature of the machine, the company ABC decides to use the sum of years’ digits depreciation method to allocate the cost of the machine over its useful life.
This can be done when you have the asset’s cost, salvage value, and useful life. While all the methods of depreciation would lead to the same result, the only variation is the time taken for depreciation nrv: what net realizable value is and a formula to calculate it recognition. The straight-line method may take much longer to calculate the depreciation expense. The method facilitates the calculation when the asset performance is at its highest.


